之前讲到了 Linux 是如何启动的,现在就写一个 UEFI 程序可以启动 Linux ,语言选择的是非常火热的 Rust 。
Linux Kernel 经过了这么多年的发展,其实完全有着 boot 的能力,使用 UEFI 启动 Kernel 其实是非常简单的一件事情,不再需要像以前 BIOS 启动老版本内核一样要把内核加载到某个内存地址,把参数放到某个内存地址,再将这个地址放到寄存器中等等复杂操作。
制作 Kernel 镜像
启动 Linux 之前我们首先需要一个 Linux Kernel 的镜像。
首先从 kernel.org 上拉取最新的 release Linux 6.5.5 :
$ wget 'https://cdn.kernel.org/pub/linux/kernel/v6.x/linux-6.5.5.tar.xz'
$ tar -xf linux-6.5.5.tar.xz
$ cd linux-6.5.5
再配置一下编译选项,要把内核编译成一个 EFI 格式的可执行文件:
$ make menuconfig
找到并进入 “Processor type and features” ,并勾选 “EFI stub support” ,。
目前的 Kernel 中 “EFI stub support” 是默认勾选,只是为了确认一下
然后就可以编译了:
$ make -j "$(nproc)"
完成之后可以看到在 arch/x86/boot/ 下有个 bzImage ,这就是编译出来的内核:
$ file arch/x86/boot/bzImage
arch/x86/boot/bzImage: Linux kernel x86 boot executable bzImage, version 6.5.5 (vandark@hustcpu01) #2 SMP PREEMPT Fri Sep 29 02:03:58 CST 2023, RO-rootFS, swap_dev 0xB, Normal VGA
构建 initramfs 和 rootfs
只是想要启动看看效果的话其实只需要复制 /boot/initramfs-linux.img 到 esp/efi/boot 中就可以了,这样的话能够进入一个使用内存当作磁盘的 Linux 环境中,但这也足以验证 Linux 的成功启动了。
编写 Rust UEFI 代码
#![no_main]
#![no_std]
extern crate alloc;
use alloc::vec::Vec;
use log::info;
use uefi::prelude::*;
use uefi::proto::device_path::build::media::FilePath;
use uefi::proto::device_path::build::DevicePathBuilder;
use uefi::proto::device_path::{DevicePath, DeviceSubType, DeviceType, LoadedImageDevicePath};
use uefi::proto::loaded_image::LoadedImage;
use uefi::table::boot::LoadImageSource;
use uefi::{
entry,
table::{Boot, SystemTable},
Handle,
};
#[entry]
fn main(image_handle: Handle, mut st: SystemTable<Boot>) -> Status {
uefi_services::init(&mut st).unwrap();
let bt = st.boot_services();
info!("Start booting...");
let mut storage = Vec::new();
let kernel_image_path = get_kernel_device_path(bt, &mut storage);
let kernel_image_handle = bt
.load_image(
image_handle,
LoadImageSource::FromDevicePath {
device_path: kernel_image_path,
from_boot_manager: false,
},
)
.expect("failed to load kernel");
// 加载 kernel image
let mut kernel_loaded_image = bt
.open_protocol_exclusive::<LoadedImage>(kernel_image_handle)
.expect("failed to open LoadedImage protocol");
// 设置参数,只设置了 initrd 没有设置 root
let load_options = cstr16!(r"initrd=efi\boot\initramfs-linux.img");
unsafe {
kernel_loaded_image.set_load_options(
load_options.as_ptr().cast(),
load_options.num_bytes() as u32,
);
}
// 启动 kernel image
bt.start_image(kernel_image_handle).expect("failed to launch kernel");
Status::SUCCESS
}
fn get_kernel_device_path<'a>(bt: &BootServices, storage: &'a mut Vec<u8>) -> &'a DevicePath {
let loaded_image_device_path = bt
.open_protocol_exclusive::<LoadedImageDevicePath>(bt.image_handle())
.expect("failed to open LoadedImageDevicePath protocol");
let mut builder = DevicePathBuilder::with_vec(storage);
for node in loaded_image_device_path.node_iter() {
if node.full_type() == (DeviceType::MEDIA, DeviceSubType::MEDIA_FILE_PATH) {
break;
}
builder = builder.push(&node).unwrap();
}
builder = builder
.push(&FilePath {
path_name: cstr16!(r"efi\boot\bzImage.efi"),
})
.unwrap();
builder.finalize().unwrap()
}
在 qemu 环境中运行:
$ mkdir -p esp/efi/boot
$ cp target/x86_64-unknown-uefi/debug/boot.efi esp/efi/boot/bootx64.efi
$ cp bzImage esp/efi/boot/bzImage.efi
$ cargo build --target x86_64-unknown-uefi
$ qemu-system-x86_64 -enable-kvm \
-m 1G \
-hda disk.qcow2 \
-serial stdio \
-drive if=pflash,format=raw,readonly=on,file=OVMF_CODE.fd \
-drive if=pflash,format=raw,readonly=on,file=OVMF_VARS.fd \
-drive format=raw,file=fat:rw:esp
OVMF 是为虚拟机开启 UEFI 支持的工具
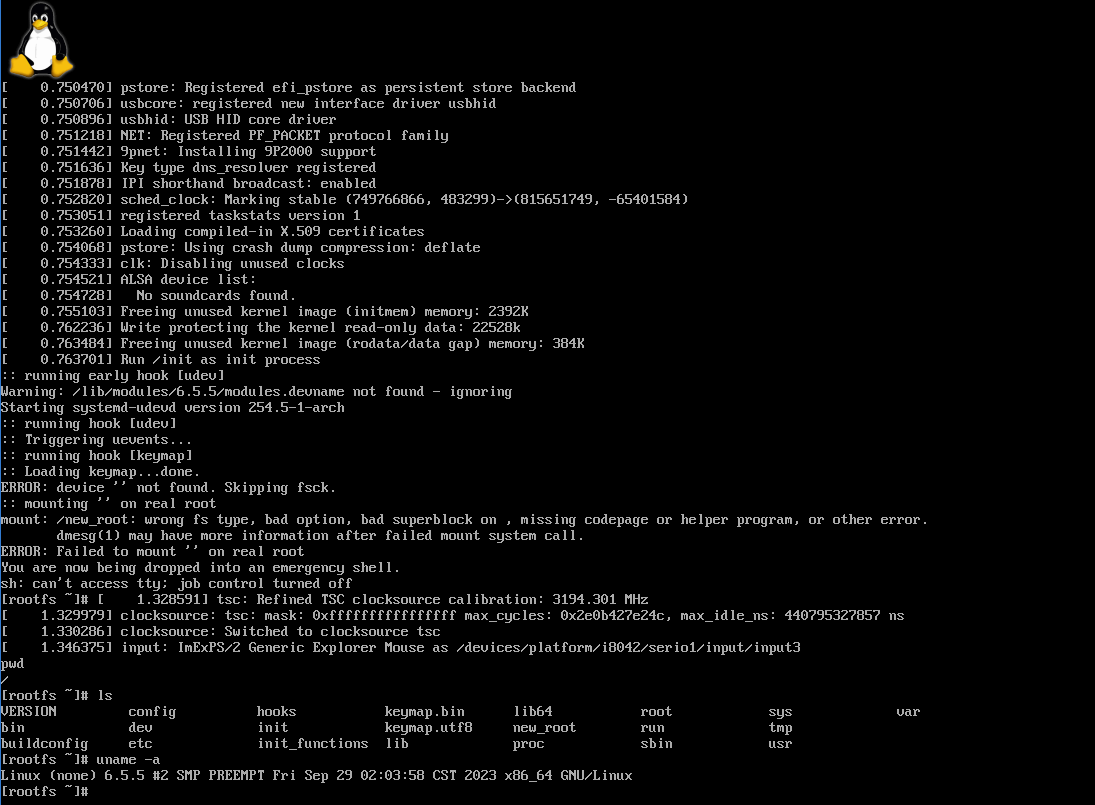
好耶!成功引导启动了 Linux !